What is Edge Computing and Why is it Important for Industrial Automation?
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that allows users to quickly process large amounts of data at the source of the data close to the edge of the network, thereby reducing the burden on cloud servers. Rather than replacing traditional cloud- or server-based data management, edge computing provides a complementary approach that improves efficiency by reducing data transmission latency and enhancing bandwidth, security, and scalability. In addition, edge computing facilitates real-time analysis, data filtering, and decision-making, thereby improving the performance and efficiency of industrial automation systems.
Within the framework of industrial automation, edge computing coincides with various technologies such as SCADA, PLC, IPC, HMI, etc. These technologies, as edge devices, can communicate with each other and with central servers or clouds. They can work simultaneously, independently, or in a distributed manner.
Edge devices are able to run applications or algorithms customized for processes such as data compilation, compression, encryption, filtering, and evaluation. Edge computing also facilitates interaction between devices and controllers, applying data processed at the edge of the network.
Advantages of Edge Computing in Industrial Automation
- Efficiency: Edge computing enables organizations to process large amounts of data quickly where the data is collected. This strategy is more efficient than sending all collected data to a distant cloud or data center, a process that can result in significant network latency and performance issues.
- Reduced response time: Edge computing can help industries process data faster and more reliably, ideally in real time. Edge computing enables devices close to the edge of the network to instantly alert relevant personnel and equipment about mechanical failures, security threats, and other critical events, facilitating rapid corrective action.
- Data sovereignty: When handling customer data (collection, processing, storage, and utilization), organizations must comply with specific data privacy regulations in the country or region where the data is collected or stored. Edge computing can help companies maintain compliance with local data sovereignty regulations by processing and storing data where it is collected.
- Cost-effectiveness: Edge computing can help companies cut IT expenses by processing data locally instead of relying on cloud services. This not only reduces costs associated with cloud processing and storage, but also cuts the overall cost of data transmission by eliminating unnecessary data at the point of collection.
The Importance of Automated Edge Controllers
Edge controllers can play a decisive role in industrial automation. Modular systems offer suitable solutions for sensor interfaces. Signals can be reliably collected from the field level and managed locally on the factory floor. Edge controllers with different communication interfaces and fieldbuses can be used to collect this data horizontally from manufacturer-independent devices via CANopen, Profibus DP, EtherNet/IP or Modbus-TCP, and can also manage vertical information via MQTT and OPC UA protocols.
Edge controllers can be incorporated into existing automation systems as scalable nodes and gateways that can be retrofitted without interfering with the actual automation process. The data can then be aggregated into summary information and transmitted to a higher level, such as MES or the cloud. In this framework, the advantages associated with a cloud link initially appear very promising, since cloud solutions are flexible, scalable, highly available and offer the opportunity for centralized access.
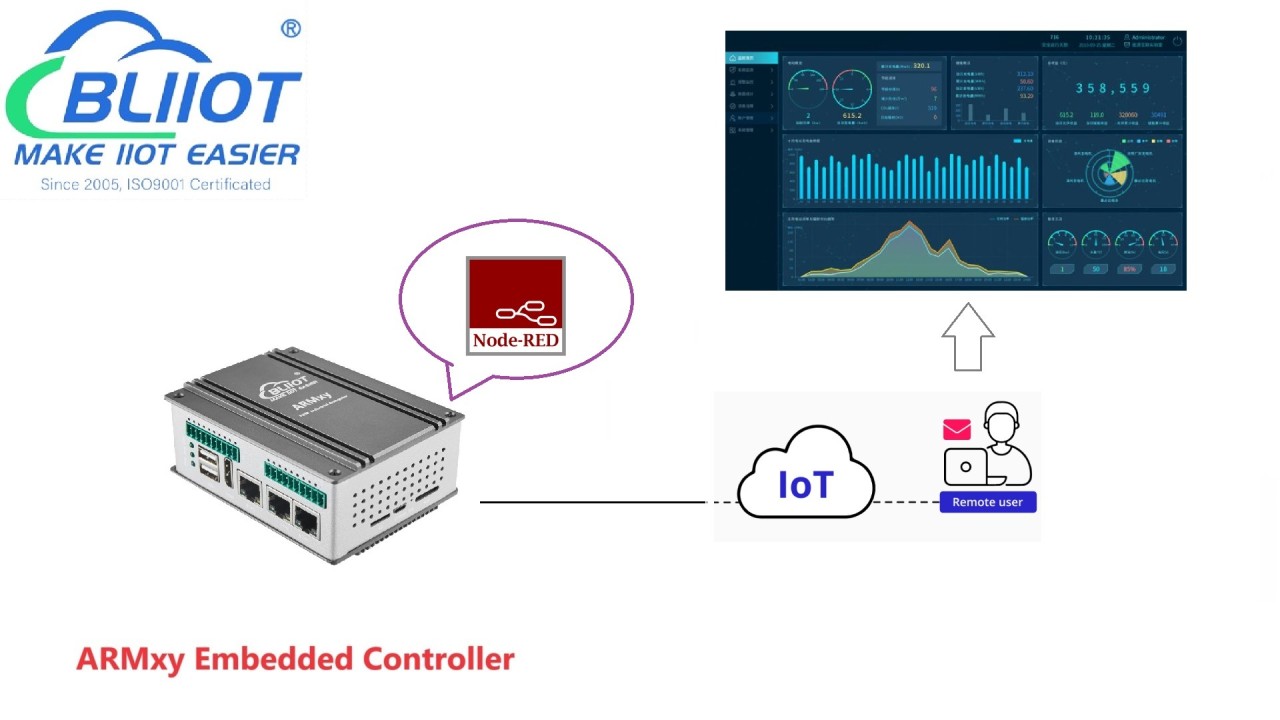
BLIIoT ARM Edge Controllers ARMxy Series BL340

The ARMxy BL340 series is a versatile industrial ARM controller designed for flexible I/O configuration. Provides a wide range of interfaces, including 1 x 1000Mhz Ethernet port, 2 x optional 100Mhz Ethernet ports, 2 x USB 2.0 ports, 1 x optional HDMI 2.0a port, 1 x optional X-series IO board, 2 x optional Y-series IO boards. These interfaces support various functions such as communication, PWM output, pulse counting, and data acquisition and control.
BL340 is compatible with BLIoTLink industrial protocol conversion software for data collection and transformation, and can seamless integrationwith various mainstream IoT cloud platforms and industrial SCADA software. Users can leverage the BLRAT for remote access and maintenance of the BL340 embedded computer. Additionally, with support for Node-Red, users can rapidly develop IoT applications on the BL340.
The Future of Edge Computing
As industrial automation grows, edge computing will likely grow in importance. Today, hybrid models that combine edge computing and cloud computing are most prevalent, with edge computing primarily used for initial tasks such as data filtering and classification.
Looking ahead, we can expect to see the development of more edge computing use cases and a shift toward truly decentralized control technologies. As processes become more streamlined and defined, edge computing will likely play an increasingly important role in our automated future.